Nội dung
1. Common leachate treatment methods.
For leachate treatment, the common process includes the following methods:
1.1 Pretreatment.
pH balancing: is a method of adjusting the pH of leachate to create favorable conditions for subsequent treatment processes.
Solid separation: removal of large suspended solids by processes such as mechanical filtration, sedimentation or membrane fiber filtration.
Oil and grease separation: removal of oil, grease and fat by using methods such as oil filtration, oil sedimentation or de-oiling processes.
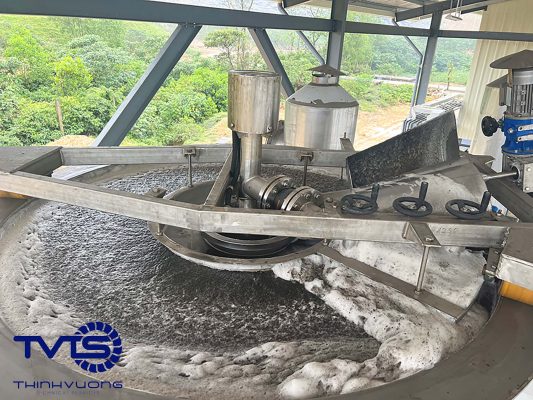

Coagulation and flocculation (physical and chemical) process: using chemicals to precipitate pollutants such as heavy metals or phosphorus in leachate.
Adsorption process: using adsorbents such as activated carbon to remove organic substances, color and odor in leachate.
1.2 Biological treatment:
Anaerobic biological process: using microorganisms to decompose organic substances in leachate. Microorganisms destroy organic pollutants in an oxygen or oxygen-free environment.
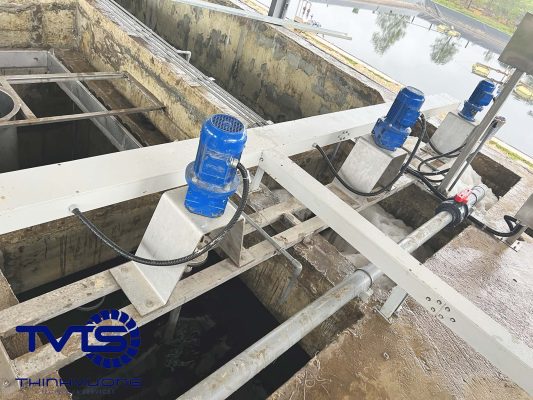

Biological pond process: creates living environments for microorganisms in lakes or ponds. Microorganisms will decompose organic matter and pollutants in leachate.
1.3 Membrane treatment:
RO (Reverse Osmosis) membrane: uses pressure to push water through a semi-permeable membrane to remove pollutants, salts and impurities in leachate.
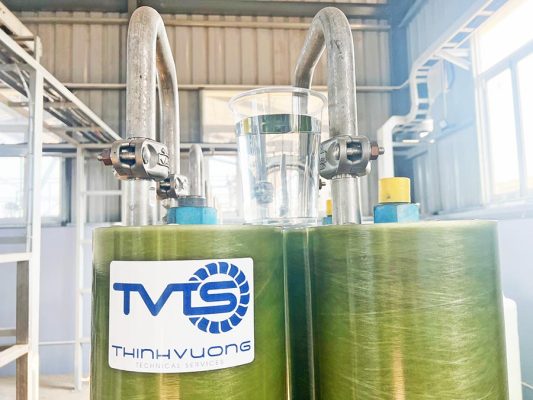

UF (Ultrafiltration) membrane: uses a membrane with small filter holes to remove large particles, bacteria and microorganisms from leachate.
NF (Nanofiltration) membrane: uses a membrane with smaller filter holes than UF membrane but larger than RO membrane to remove organic substances, small molecules and salts in leachate.
1.4 Disinfection:
Using disinfection methods such as using chemical products, ultraviolet rays or ozone to kill bacteria, viruses and pathogens that may be present in treated water.
1.5 Water quality adjustment:
PH balancing: is a method of adjusting the pH of water after treatment to achieve a suitable pH level for use or discharge. Pond bottom treatment removes scum and sediment from the lake or treatment pond.
The leachate treatment technology process can combine many different steps and methods depending on the specific requirements and scale of the system. TVTS is proud to have a team of experts and engineers with rich experience in designing and operating the system accurately to ensure efficiency and compliance with environmental regulations.
To better understand the design and operation of the leachate treatment system. We will present the leachate treatment solution at a specific project that we have implemented in the following content.
2. The most optimal leachate treatment technology process for a specific project.
2.1. Identify and analyze the investor’s requirements.
The leachate treatment technology is applied with advanced technology to meet the requirements of customers. The factory wants to be the leader in treatment technology in the industry, building prestige and competitiveness with competitors in the same field.
The operating capacity is 250 m3 / day and night.
The leachate quality parameters before treatment include:
- pH value: 6.7,
- COD 5,000mg/L,
- TSS: < 250 mg/L,
- CL-: 2,000 mg/L,
- TDS: 8,000 mg/L.
The clean water recovery rate is from 50% to 70% of the total leachate capacity.
We propose to use STRO membrane technology specializing in leachate treatment. STRO membrane is exclusively provided by TVTS, providing a comprehensive solution, helping to thoroughly treat landfill leachate in a simple and effective way. Increase the water recovery rate up to 75%.
2.2 The most optimal leachate treatment technology process in 2023.
After studying the actual project and the requirements set by the investor. TVTS Company proposes the most optimal leachate treatment technology process in 2023 for the factory, including the following water treatment steps:
Description of the most optimal basic leachate treatment technology process in 2023.
- Coarse filtration of large substances from leachate: The leachate will be filtered of large substances and go into the collection tank. Here, the leachate is stabilized before entering the treatment process.
- The wastewater is then transferred to the equalization tank to participate in the aeration process. This helps reduce the concentration of wastewater and avoid causing anaerobic reactions that cause odors.
- After the equalization tank, the wastewater is pumped into the physicochemical tank to carry out the first and second level physicochemical processes. The physicochemical process is the flocculation process using coagulants. Here, the concentration of suspended solids, BOD, COD in the water is significantly reduced.
- In the physicochemical settling tank, the sludge is separated and taken to the landfill.
- Water from the physicochemical settling tank after separating the sludge, meeting the input standards of the RO system, is filtered at high pressure. Here, the wastewater is almost completely removed of minerals, substances, impurities, bacteria, viruses, … only clean water is recovered.
- The sludge after the RO system will also be returned to the landfill.
- Clean water after RO meets the prescribed discharge standards. Can be reused for suitable purposes. Water will be disinfected if necessary before use.
Flow chart of leachate treatment technology.
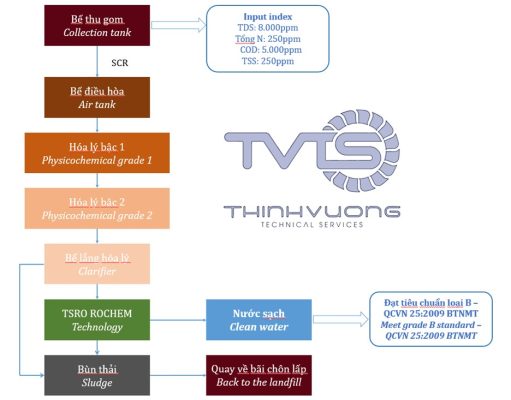
With the above leachate treatment technology process, the factory can meet the strict requirements of customers on water quality and at the same time minimize negative impacts on the environment.
3. Why choose STRO membrane for the calculation of leachate treatment technology?
TVTS’s STRO Membrane Module System is the optimal solution for leachate treatment technology. With the Frame – Disc membrane module system (Triple S Module), TVTS’s STRO membrane is designed with an open channel filter that allows the system to separate waste streams with high COD, BOD without causing membrane clogging.
3.1 Advantages of TSRO ROCHEM membrane.
This is the only module line in the world with the highest resistance and operates at high pressure. The processing capacity of TVTS’s STRO membrane is guaranteed to be the highest compared to other membrane units. It operates on high wastewater with COD/BOD up to 140,000 ppm.

Membrane systems are used to thoroughly treat wastewater with very high COD and BOD. Suitable for industries such as Landfill, Distillation, Pharmaceuticals, Textiles, PCB production, chemical and nuclear waste.
Feasibility in using Frame-Disc Membrane technology is superior to other methods such as evaporation and secondary treatment.
3.2 The basic advantages of Frame-Disc Membrane technology are:
- Minimizes fouling.
- Can handle high TSS, COD, BOD and wash water treatment in all industries.
- Lowest operating costs and long membrane life.
- Proven technology worldwide.
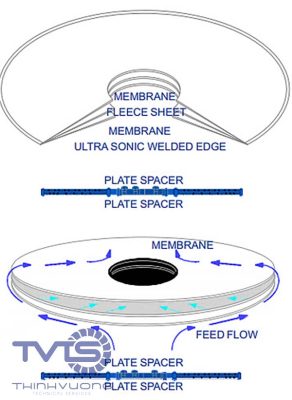
The effectiveness of the design of the leachate treatment line with a capacity of 250 m3/day and night has been proven in practice. Currently, the system has been put into operation and is operating stably. The quality of the water after treatment always meets the prescribed standards.
3.3 Some landfill and TVTS projects applying STRO technology have been proven effective such as:
In Vietnam:
Da Phuoc, Ho Chi Minh City: capacity 280 m3/day, 2007.
Nghi Son, Thanh Hoa: capacity 150 m3/day, 2013.
Thien Phuoc, Dong Nai: capacity 100 m3/day, 2016.
Thuy Phuong, Thua Thien Hue: capacity 250 m3/day, 2022.

And many other locations around the world:
– Deponie Ihlenberg – Selmsdorf, capacity 1,200m3/day, 1989.
– Grobdeponie Halle – Lochau, Germany: capacity 408m3/day, 2000.
– Zentradeponie Burgdorf, Germany: capacity 900m3/day, 2000.
– Deponie Helvesiek, Germany: capacity 65m3/day, 2000.
– Abfallentsorgungsanlage, Germany: capacity 79m3/day, 2001.
– Johannistal, Germany: capacity 72m3/day, 2001.
– Yecheon Landfill, Korea: capacity 53m3/day, 2012.
If you need more detailed information on the leachate treatment process or need technical support in related areas at your factory. Please contact customer service for the earliest support.
We would like to thank you and look forward to sharing this useful information with those interested in leachate treatment ./.



