Nội dung
- 1. Overview of the circular economy
- 2. Distinguishing between circular economy and linear economy (CEE)
- 3. Circular economy models
- 4. KTTH in the world and in Vietnam
- 5. Circular economy in enterprises
- 6. Criteria for evaluating circular economy implementation
- 7. Some other content related to circular economy that readers may be interested in
1. Overview of the circular economy
1.1 What is a circular economy? What is a circular economy?
Concept of a circular economy (KTTH): Circular economy is an economic activity in which design, production and services operate with the goal of extending the life of materials and products, thereby eliminating negative impacts on the environment. By recycling, reusing, and regenerating raw materials, fuels, and materials involved in economic activities.
The question is what is a circular economy. Is doing business with the purpose of maintaining the value of materials for the longest time. Thereby helping to minimize or eliminate emissions into the environment.
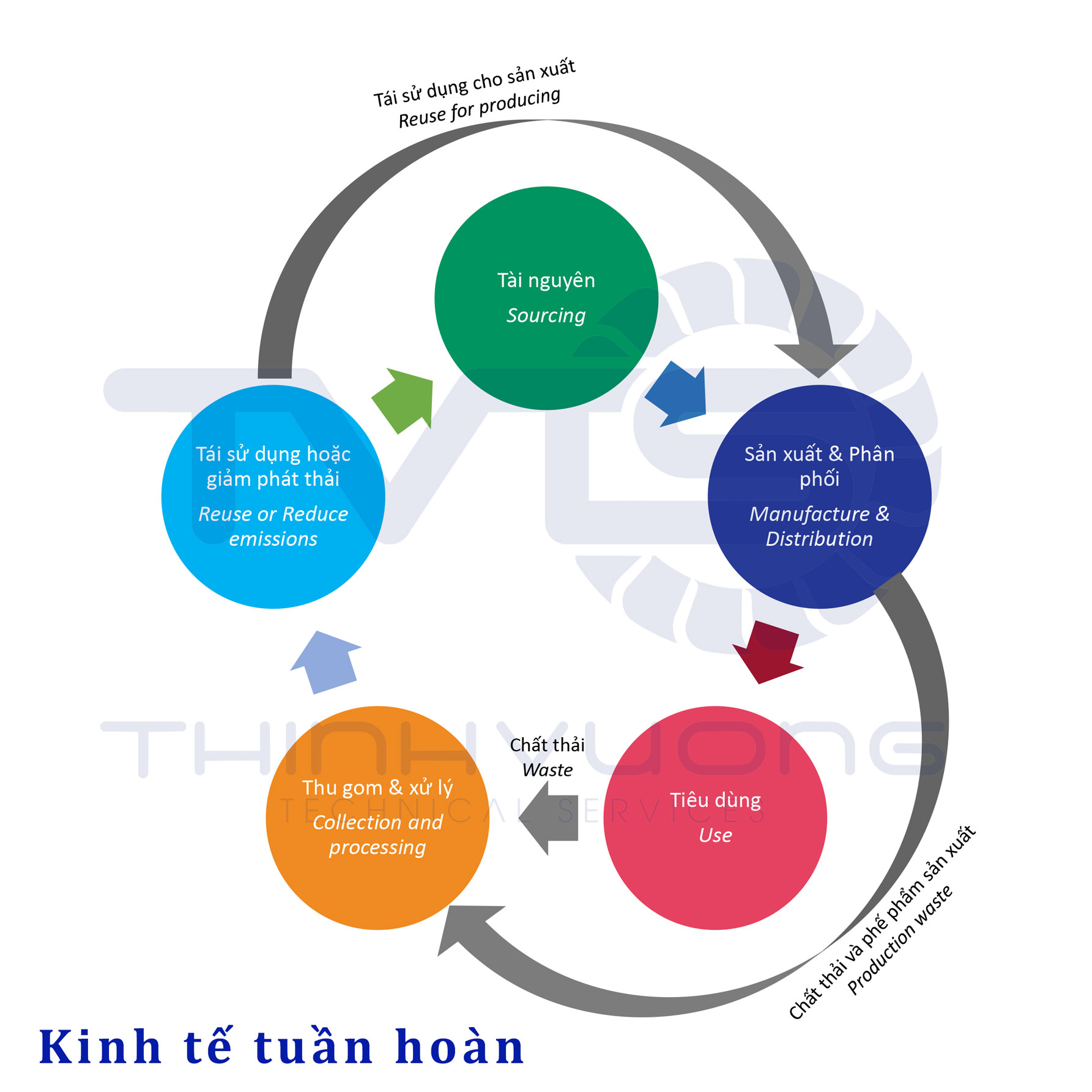
Circular economy or circular economic model is the state that builds the country’s economy to develop in the direction of circular economy. It has the following characteristics:
- Reduce raw material consumption, reduce emissions during production and operation. Circulate water, raw materials, fuels, materials and products.
- Return to the soil and water ecosystem what has been exploited.
- The energy used is renewable energy, clean energy.
- Raw materials and fuels emit low CO2.
- Minimize the use of toxic chemicals in the production line.
- Extend the life and life cycle of products.
1.2 Circular Economy in English is “Circular Economy”.
Circular Economy is accompanied by other phrases in English such as: Reuse; Recycle; Restorative; Regenerative; Zero carbon.
1.3 Benefits of Circular Economy
1.3.1 For consumers
Consumers can use products of higher quality and non-toxicity. Because the production process when using recycled materials will be more strictly controlled. The product’s lifespan will be increased, which means saving costs in the long run.
1.3.2 For businesses
Recycling, reusing raw materials as well as limiting energy use will save costs for businesses in the production, promotion and sales process.
Circular Economy helps solve the problem of excess products while lacking resources. Create motivation for businesses to invest and innovate to increase product value. This helps reduce production costs and increase the supply chain, ….
1.3.3 For the country
Circular economy helps solve global challenges of environmental pollution and climate change. At the same time, it improves capacity and competitiveness in the international arena.
Used raw materials instead of still spending costs on processing and disposal. Now continue to be processed and used for another purpose. Make full use of the value of exploited natural resources. Minimize the amount of waste released into the environment.
1.3.4 For society and the environment
Circular economy helps reduce social costs in environmental management, protection and response to climate change; create new markets, ….
In general, successful implementation of the circular economy will solve most negative problems for the environment and ecosystem.

- Solve the problem of natural resource depletion.
- Improve environmental health, enhance biodiversity and species degradation.
- Solve the problem of carbon emissions, greenhouse gas emissions, …
2. Distinguishing between circular economy and linear economy (CEE)
When referring to the macroeconomic terms CEE and CEE, we must have a basic understanding of the difference between these two economic models.
Linear economy is an economy that develops in a straight line. Economic development is promoted and benefits from raw materials, fuels and materials. Waste and surplus after production are discharged into the environment.
Meanwhile, CEE is an economic development model in which production is focused on creating high-quality products. At the same time, waste and surplus products created need to be processed and reused in a circular manner. Production can be put into a closed process to minimize waste to the environment.
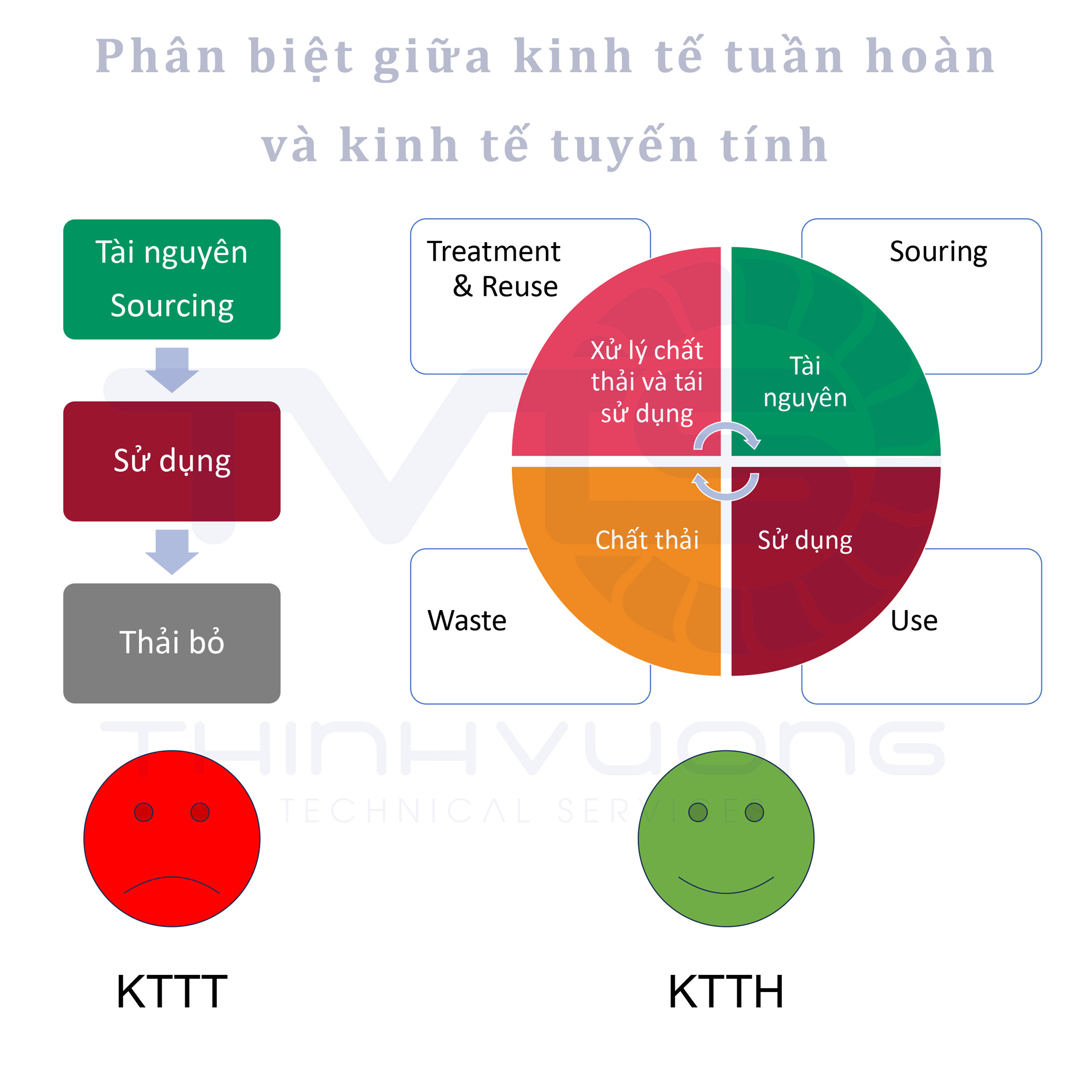
3. Circular economy models
The circular economy model is specifically demonstrated at each manufacturing plant. Or according to the regulations and institutions of a locality or a region. Each different country will have different circular economy models to suit socio-economic development.
3.1 Three pillars of the circular economy
In Vietnam, according to the 2020 revised Law on Environmental Protection, Article 142 on circular economy.
Excerpt: “Circular economy is an economic model in which design, production, consumption and service activities aim to reduce the exploitation of raw materials and materials, extend the product life cycle, limit waste generation and minimize negative impacts on the environment”.
According to Dr. Nguyen Hoang Nam (Head of the Circular Economy Department at the National Economics University), the development of the circular economy needs to pay attention to 3 pillars: institutions, techniques, and awareness.
So, the three pillars of the circular economy are understood as:
- Institutions, regulations, and policies of the host state on the application of circular economy.
- Economic development model in the direction of circularity. Authorities, enterprises and factories always research and propose solutions on green production. Reduce emissions, recycle, reuse.
- Raise awareness of the implementing community. Agencies and management boards of establishments have good policies, so helping individuals to implement have good awareness in the policy. This is also considered one of the three important pillars of the circular economy.
3.2 Some solutions to promote circular economy are of interest
Solutions to promote circular economy are to propose ways to implement well the three pillars of circular economy. Such as:
Amending and supplementing environmental laws related to circular economy. Creating specific and strict legal institutions to facilitate the monitoring and implementation process.
Developing circular economy is closely linked to the development of technology, the 4.0 economy. Through this, propaganda to raise awareness of each citizen. So that they understand the important meaning of recycling and protecting natural resources. From there, there is compliance with the law, not for profit but cheating.
In the form of micro enterprises or factories. There are always new production methods, taking advantage of surplus materials and waste to make raw materials for one or more other production processes in the factory. Pay special attention to the reuse of wastewater because this is a popular solution and brings a lot of efficiency to large enterprises in the world and in Vietnam.
And more, ….
4. KTTH in the world and in Vietnam
4.1 KTTH in the world
Philips is a prestigious brand from the Netherlands. Changing from selling lighting products to selling lighting hour services. For each light bulb product, the company sells a service with an operating time of 3000 hours, after which the manufacturer will collect the product and recycle it to continue the next life cycle of the product.

4.2 Circular Economy Development Project in Vietnam
In Vietnam, the implementation of circular economy is institutionalized in the Law on Environmental Protection 2005. The law reflects the extended producer responsibility (EPR) including responsibility for input and output products of the production process. Recycling and reducing emissions as well as responsibility for substances released into the environment.

However, EPR in the 2005 Law on Environmental Protection has not been effective because it is still voluntary.
By 2020, the Law has been amended to improve the effectiveness of EPR implementation. The collection and treatment of waste from the production process or importer is regulated as a responsibility, and is compulsory for certain groups of waste. (Specifically in the 2020 Law on Environmental Protection).
This change is consistent with the Party and State’s policy of developing circular economy. At the same time, it is consistent with international practices on green economy, emission reduction and environmental protection.
EPR is an effective tool in waste management in the world. Currently, there are about 400 EPR systems in different countries being applied and bringing high efficiency to economic and environmental development (source: dangcongsan.vn).
4.3 Circular economy in agriculture
When the linear economy is developing strongly to accelerate the industrialization and modernization process in each country. Then somewhere the circular economy has crept into agriculture and brought about very high efficiency. That is the V-A-C agricultural model.
Perhaps V-A-C is no longer too strange. Appearing in the textbooks of the Ministry of Education and Training in grades 3/12. V-A-C is very simple, easy to understand and easy to implement. But brings very high economic efficiency to farmers.
Currently, the circular economy in agriculture is strongly promoted through the policies and guidelines of each province and district. Policies encourage farmers and businesses to participate in recycling agricultural by-products. Local authorities award certificates of merit for creativity and commendation for individual and collective achievements in applying the circular economy.
The cultivation sector has always played an extremely important role in agriculture. It helps ensure national food security, provides raw materials for production, ….
Cultivation applying circular economy requires connecting the entire system, a closed cycle from production – processing – consumption – waste and by-product management.
Some circular economy applications in agriculture such as:
- Utilize by-products in rice cultivation such as straw and stubble as raw materials for mushroom cultivation and organic fertilizer.
- Coffee husks are used as fuel, and the ash after burning is used as raw material for unburnt brick production. Or coffee husks are used directly as fertilizer.
- After the agricultural production process to get products. The by-products will be utilized to the maximum or treated to ensure safety before returning organic matter to the soil.
4.4 Circular Economy in Construction
The construction sector uses a huge amount of natural resources. Raw materials such as soil, sand, and stone are second only to fresh water. Energy use is 33% and emissions are 39%. ….

Construction development goes hand in hand with infrastructure and national development. Therefore, this sector needs to be prioritized and have specific regulations in monitoring development in the direction of circular economy.
Some possible solutions for the construction industry:
- For businesses supplying raw materials for construction, they should switch from low-carbon products to high-carbon products. For example, using bricks from lightweight, recycled materials instead of red bricks fired from clay.
- Using waste output from one manufacturing industry as raw materials for another manufacturing industry. For example, using SO2 in coal-fired thermal power as raw materials for cement and plaster production.
- Tiles, design bricks using recycled materials, etc.
4.5 Some circular economy seminars in Vietnam
There have been many circular economy seminars in Vietnam. The program is organized by universities, conference centers, and relevant state economic agencies. The topic is a comprehensive circular economy orientation or in the fields of construction, textile dyeing, food, pharmaceuticals, etc.
For more information about circular economy seminars, readers can refer to the websites of VCCI, WETV, etc.
5. Circular economy in enterprises
Circular economy brings benefits to all enterprises and factories that apply it. Developing this economic model is very promising and necessary. The task of finding solutions to reduce emissions to the environment is a common task of society. And it is also to protect our own homes.
The manufacturing industry that can easily apply and benefit from applying circular economy is the paper and packaging sector. Waste from many other manufacturing industries and from human life, including paper and plastic, is recycled and meets safety standards. Then it is circulated in the production of other paper and plastic products.
Leading in this field is Pro Vietnam. This is the Vietnam Packaging Recycling Alliance. The association consists of 21 companies (2023), working with the state to improve and enhance the quality of the packaging recycling process. Improve the quality of life and the environment in Vietnam.
In addition to Pro Vietnam, there are also many production units that have successfully applied circular economy. A specific example is Vinamilk.
5.1 Vinamilk’s circular economy model
Waste from dairy farms is put into septic tanks (biogas tanks) for treatment. The treatment process produces two types of waste: methane gas and sludge.
+ Methane gas is used as energy to heat water, pasteurize milk and dry grass for storage.
+ Treated sludge is used as fertilizer and soil improvement.
The resulting efficiency helps Vinamilk save billions of VND each year.
In addition, KTTH is also applied between farmers and factories. Specifically, farmers provide food sources for the farm such as grass, corn, etc. In return, the factory will support farmers with fertilizers, equipment for cultivation, etc.
In 2022, Vinamilk was voted as one of the 5 “Enterprises that effectively implement the circular economic model and respond to climate change” (At the Ceremony to announce sustainable enterprises in Vietnam 2022).
5.2 Water treatment solutions at TVTS participate in the circular economic model
Thinh Vuong Technical Services Joint Stock Company operates in the field of water and wastewater treatment. We always understand the importance of water, Spending many years on treatment technologies. TVTS has provided suitable water treatment solutions for the factories we accompany.
We accompany the factory in each stage of development. In the first stage, the factory only required wastewater treatment to meet discharge standards, until now it is the stage of upgrading to reuse or recycle water for production processes.

Greening the business with water recirculation solutions helps factories achieve important standards in exporting products to countries around the world. Especially in the textile dyeing industry.
Current wastewater treatment solutions participating in the circular economy that TVTS provides include:
- Wastewater reuse solution.
- Zero liquid discharge solution- ZLD.
6. Criteria for evaluating circular economy implementation
Each production and business sector will have its own set of criteria for evaluating circular economy implementation. However, these criteria are built on the effectiveness in implementing “reducing the exploitation of raw materials, materials, extending product life cycles, and limiting waste generation”.
6.1 Example in the construction sector
The Green Building Council VGBC (Lotus) has developed a table to evaluate raw materials on a 15-point scale. Of which, 5 points are for sustainable materials, 2 points for dismantling and construction waste management, and 8 points for innovative solutions.
VGBC develops a sustainable economy in parallel with the following criteria:
- Recycling and reuse.
- System products are easy to repair, reuse and disassemble.
- Prioritize the use of recycled materials/products.
- Create products that do not contain toxic substances.
6.2 Framework for developing a set of criteria for evaluating the implementation of a circular economy
The development of a set of criteria for evaluating implementation should pay attention to direct quantitative assessment, direct qualitative assessment, and indirect assessment of:
- Products created (features, performance, product life, etc.).
- Product accessories (necessary level, minimize if possible, etc.).
- Diversity of raw materials, and the use of safe recycled materials.
- Energy consumption level, use of green energy, recycled energy. Or use of energy from raw materials to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reference to some equivalent fields or previous countries that have implemented.
7.1. What is Iced?
Iced in the field of circular economy refers to the Institute for Circular Economy Development Research. Established in 2020. It is a public unit operating in science and technology research under the Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM).
7.2 Where is the Circular Economy Institute?
The Circular Economy Institute is located at:
Thu Duc City: Room 103 – 104, Building A, VNU-HCM Software Technology Park, Linh Trung Ward, Thu Duc City, Ho Chi Minh City.
Ho Chi Minh City: 5th Floor, Linco Building, 61A – 63A Vo Van Tan, Vo Thi Sau Ward, District 3, Ho Chi Minh City.



