Landfill leachate (Leachate in English) is Landfill leachate.
Leachate concept:
Leachate is wastewater generated from waste, landfills, and garbage collection sites. Leachate is a type of wastewater that seeps through waste storage areas, making it unsafe and causing environmental pollution
Nội dung
1. Origin of leachate
The main sources of leachate include water from above the landfill, moisture in the waste, and water from the covering material. The loss of water stored in the landfill includes water consumed in gas-forming reactions, saturated water vapor evaporated with the gas, and water released from the bottom of the landfill (leachate).

Stages of leachate generation:
When waste is dumped in areas such as public landfills, industrial landfills. Or areas where waste is generated improperly, the natural decomposition of waste begins to occur.
When organic waste (such as food, branches, and other organic matter) decomposes. They create leachate through the process of biological decomposition. The biological decomposition process creates leachate rich in organic matter and nutrients.
In addition, leachate can also originate from the drainage process from landfills. When rain falls on landfills or water is added to create decomposition conditions, the water will flow through the layers of waste and collect other waste and pollutants, forming leachate containing chemical compounds and bacteria.
There are many different sources of leachate. Generally, they are generated from waste. Wherever there is waste, there is the potential for leachate to arise. The need for treatment according to regulations depends on the concentration and volume of leachate large enough to perform.
In addition, leachate to the landfill and treatment process must ensure safety. Strictly comply with regulations on collection, transportation, treatment and discharge equipment.
2. Composition and properties of leachate
2.1 Characteristics of leachate
The characteristics or composition of leachate depends on the origin and composition of waste in the waste storage area. Some characteristics are:
- Color: Leachate is usually dark in color, from brown to black.
- Odor: Leachate often has an unpleasant odor due to the decomposition of organic matter and the presence of odor-causing bacteria.
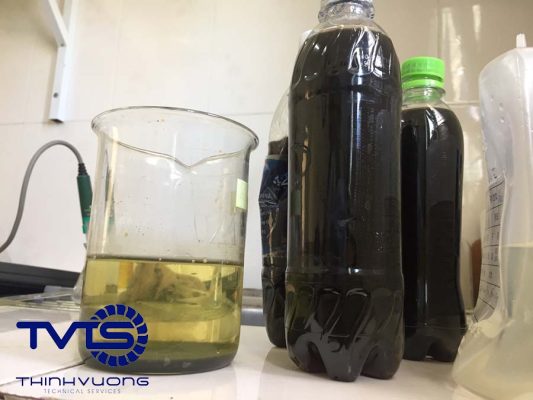

- pH: The pH of leachate is low or high depending on the composition of the waste. For example, leachate from a landfill containing industrial waste may have a low pH due to the presence of acids, while leachate from a landfill containing organic waste may have a high pH due to the decomposition of organic matter.
- Organic matter: Leachate often contains a large amount of organic matter, including organic compounds that decompose from waste. This organic matter can affect water quality and the treatment process.
- Chemical compounds: Leachate can contain toxic chemical compounds such as heavy metals, organic pollutants, and additives from industrial waste. These compounds can be harmful to the environment and health if not treated properly.
- Bacteria and microorganisms: Leachate often contains different types of bacteria and microorganisms. These bacteria can cause the decomposition of organic matter and create odors, and can also carry infectious diseases.
2.2 Some water quality indicators and components of leachate of interest
The quality of leachate changes at different temperatures. The leachate temperature is the water temperature in the environment containing leachate. It will change according to the temperature range during the day, season and altitude.
The following content will also answer some related questions such as:
- What is the composition of leachate in Vietnam?
- What is the composition of leachate waste
- Cad file of landfill leachate monitoring well?
2.2.1 BOD index in leachate
The BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) index in leachate measures the amount of oxygen needed by microorganisms to decompose organic matter in a water sample.
The pollution level of leachate is usually considered high if the BOD index is high. That is, the water contains a lot of organic matter that is difficult to decompose. Then microorganisms need to consume a lot of oxygen to process those organic matter.
The BOD index in leachate ranges from 100 – 60,000 ppm. At landfills, the value of the pollution index varies depending on the composition of the waste and the age of each landfill.
2.2.2 Forms of organic nitrogen in leachate
a) What types of nitrogen are in leachate?
The answer is: Leachate can contain many types of nitrogen. Mainly in the form of nitrate and nitrite compounds.

Nitrate (NO3-) is a common form of nitrogen compound found in leachate. It is often present when organic matter, such as manure, animal waste or organic fertilizers, decomposes in an aquatic environment.
Nitrite (NO2-) is another form of nitrogen compound that can be present in leachate. Nitrite is often present when nitrate is converted to nitrite by bacteria during water management or waste treatment.
Ammonia (NH3-) is another form of nitrogen compound commonly found in leachate. It can be produced by the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen or from the decomposition of animal waste.
b) What are the organic nitrogen compounds found in leachate?
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxylic acid group (-COOH). They are often derived from organic waste such as food waste, organic fertilizers, or other biological substances.
Proteins are complex organic compounds consisting of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Proteins are made up of amino acid chains containing the chemical element nitrogen. Proteins that are not consumed or broken down will be discharged in the waste and into the leachate environment.
Urea ((CO(NH2)2)) is an organic compound containing nitrogen that is often found in leachate. It is a waste product of the metabolism of proteins and amino acids in the body of animals, including humans.
Amines are organic compounds containing an amino group (-NH2). They are produced from pesticides or industrial waste.
2.2.3 Coliform content in leachate
The coliform content in leachate is assessed by counting the number of coliform bacteria present in a unit volume of water. Usually reported as the number of coliforms per unit of measurement such as CFU/100 mL (colony-forming units per 100 milliliters).
The coliform content in leachate usually ranges from 2×106 to 10×106 CFU/100 mL
Coliform is a group of bacteria that can live and develop in the intestinal environment of humans and mammals. Therefore, the coliform content index in leachate is very important for the quality of water after treatment.
According to QCVN 25:2009 BTNMT and QCVN 40:2011 BTNMT, the allowable concentration of coliform in water after treatment is 3000 CFU/100 mL for type A discharge standard. And 5000 CFU/100 mL for type B discharge standard.

3. Formula for calculating leachate flow.
Establishing an investment project and designing the operation of a sanitary landfill. It is necessary to calculate the exact amount of leachate, from which to design a suitable leachate collection and treatment system. Ensure that the system is not overloaded or lacks water for treatment.
The amount of leachate is one of the very important factors in using it as a basic database, serving the process of proposing, calculating and improving the treatment technology, so that it is most suitable, effective and economical.
To calculate leachate accurately, we need to understand the factors affecting the amount of leachate in the landfill area.
3.1 Factors affecting leachate flow.
– Meteorological and hydrological conditions.
– Terrain.
– Geology.
– Climatic conditions.
– Rainfall.
3.2 How to calculate leachate load
Leachate calculation formula:
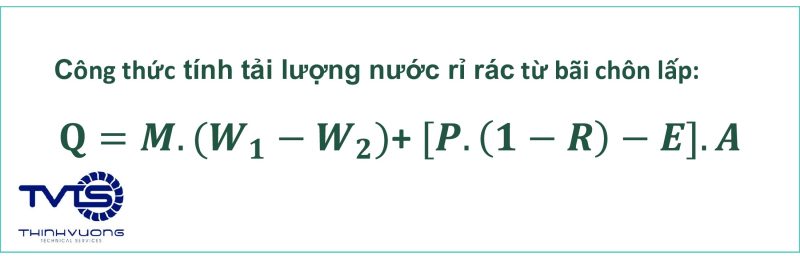
Q1 = M*(W1 -W2) + [P*(1-R) – E]*A
In which:
– Q1: Is the amount of leachate generated in the landfill cell (m3/day);
– M: Average daily volume of landfill waste (m3/day);
– W1: Humidity of waste before landfill (%), take 60%;
– W2: Humidity of waste after compression (%) take 25%;
– P: Average daily rainfall in the largest month (mm/day)
3.3 Example of calculating leachate volume of landfill in Thua Thien Hue Province.
According to the statistics of the Thua Thien Hue Hydrometeorological Station. The largest average rainfall at the Hue monitoring station in the area is 584.5mm/month (September, 2018-2019). Equivalent to 32.5mm/day.
– R: Surface drainage coefficient 0.15.
– E: Evaporation rate is taken as 5 mm/day (usually 4 – 6 mm/day).
– A: Working area per day (m2).
(According to the Textbook on Solid Waste Management and Treatment – page 342. Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Van Phuoc. Hanoi Construction Publishing House – 2014).
During the phase of this project, the treatment capacity is 195 tons/day. Based on the Solid Waste Management Plan of Thua Thien Hue Province to 2030. (Vision to 2050). The density of domestic waste on regular transport vehicles ranges from 0.2 to 0.4 tons/m3. The selected density of unrolled waste is 0.333 tons/m3. Therefore, the average volume of waste is 195/0.333 = 585.6 m3/day.
Take the rolling coefficient as 0.5. The average volume of landfilled waste per day after rolling the base is 585.6×0.5 = 292.8m3/day.
Applying the formula, we can calculate the total amount of landfill leachate as:
Q1= 292.8*(60%-25%) + [0.0325*(1-0.15) – 5/1000)]* 2,000
= 147.73 m3/day.
Therefore, the volume of leachate per hour is Q1’=147.73/24h = 6.15 m3/h.
The design and construction of the landfill leachate collection system must pay attention to calculating the amount of leachate. Avoid overloading in the rainy season, overflowing into the surrounding area. Polluting the environment and negatively affecting human health.
4. Impacts of leachate
4.1 Impacts on groundwater
Leachate seeping into groundwater will cause impacts such as:
4.1.1 Groundwater pollution
Leachate contains pollutants such as toxic chemicals, heavy metals, organic substances and other pollutants. When leachate seeps through the soil layer and comes into contact with groundwater, these pollutants can spread into groundwater and contaminate the water source.
4.1.2 Dynamic imbalance
Leachate seeping into groundwater will change the soil structure and hydrological properties of groundwater. Thereby reducing the drainage capacity of the soil, increasing groundwater pressure and changing the flow of water in the underground environment
Therefore, causing a dynamic imbalance can cause landslides. Causing land subsidence and changing the habitat of animals and plants.
4.1.3 Loss of clean water sources
Groundwater is often used as a source of clean water for humans, and other economic activities such as agriculture and industry. If groundwater is contaminated by leachate, it will no longer be safe for use.
4.2 Harmful effects of leachate from landfills
In addition to the negative impacts on groundwater. Warning of leachate pollution is very toxic, including:
Landfills produce toxic gases such as methane and volatile organic gases. Causing odors and affecting the quality of the surrounding air.
In addition, leachate from landfills can overflow into rivers, lakes. And land near the landfill area, causing environmental pollution.
Leachate from landfills can contain toxic chemicals and disease-causing bacteria. When people come into contact with this water through the use of groundwater or direct contact. Risk of causing health problems such as gastrointestinal infections, skin diseases, and respiratory problems.
Contaminants in leachate can also accumulate in food. This causes chronic diseases, long-term impacts on human health.
5. Leachate Market in Vietnam
Vietnam is a developing country with 99.8 million people, ranking 15th in the world. (According to data from the United Nations, 9/2023). With rapid economic and population growth. It shows that Vietnam generates a huge amount of waste including both domestic and industrial waste.
According to statistics from the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment. As of 2020, Vietnam has more than 900 planned landfills, of which less than 20% are sanitary. The rest are causing mild to severe pollution.
Through this, we see that Vietnam is lacking a waste management system. We are facing great challenges in waste management and waste treatment.
The landfill system and waste treatment methods have not met the demand. Moreover, they have not been implemented effectively. Therefore, leachate and waste sources continue to have negative impacts on the environment and people.
6. Summary.
Understand the negative impacts of leachate on human life and the environment.
Understand the difficulties in managing and treating waste and leachate.
We started providing leachate treatment services in Vietnam since 2013. TVTS has researched and applied advanced technology from European countries in leachate treatment. Solving difficult problems for the largest landfills in Vietnam. (Some typical leachate projects that TVTS has implemented).

With advanced technology and many years of experience, TVTS is confident to provide the best leachate treatment service at the most competitive price in the market to customers.





